Bucks traction is a crucial orthopedic treatment frequently used to manage and stabilize various musculoskeletal conditions. This article explores Bucks traction comprehensively, covering its history, purpose, indications, procedure, patient care, and advancements, ensuring you gain a thorough understanding of this non-invasive method.
Contents
- What Is Bucks Traction?
- The History of Bucks Traction
- Indications for Bucks Traction
- How Does Bucks Traction Work?
- Types of Bucks Traction
- Setting Up Bucks Traction
- Nursing Care for Patients Undergoing Bucks Traction
- Bucks Traction vs. Other Traction Methods
- Potential Complications and Side Effects
- Patient Experience and Comfort
- The Role of Bucks Traction in Orthopedics
- Advancements in Traction Techniques
- Conclusion
What Is Bucks Traction?
Bucks traction involves applying gentle, longitudinal force to an injured limb or bone. It immobilizes and stabilizes the affected area, significantly reducing pain, preventing further injury, and promoting healing. This traction method is non-invasive, meaning it does not involve surgical interventions initially, making it particularly beneficial during the acute management of certain orthopedic injuries.
The History of Bucks Traction
Introduced in the 1920s by American surgeon Dr. Charles E. Bucks, this traction method revolutionized orthopedic care. Bucks traction became widely adopted due to its effectiveness in managing fractures and injuries non-invasively. Over the decades, advancements in medical techniques have enhanced its efficacy and patient comfort, maintaining its relevance in modern orthopedics.
Indications for Bucks Traction
Bucks traction is commonly indicated for:
- Femur fractures: Particularly beneficial for managing femoral shaft fractures.
- Hip dislocations and fractures: Aids in aligning and stabilizing hip injuries before surgical intervention.
- Spinal injuries: Provides temporary immobilization to stabilize the spine, reducing further injury.
- Knee injuries: Helps stabilize injuries and reduce muscle spasms.
Its primary goal is immobilization and pain relief while preparing the injury for subsequent definitive treatment, such as surgery.
How Does Bucks Traction Work?
The mechanism behind Bucks traction involves the application of a controlled, steady pulling force. This action aligns fractured bones, reduces muscle spasms, and minimizes pain. The traction force promotes natural healing by keeping the injured limb or spine immobile and correctly positioned, facilitating the formation of new bone and tissue.
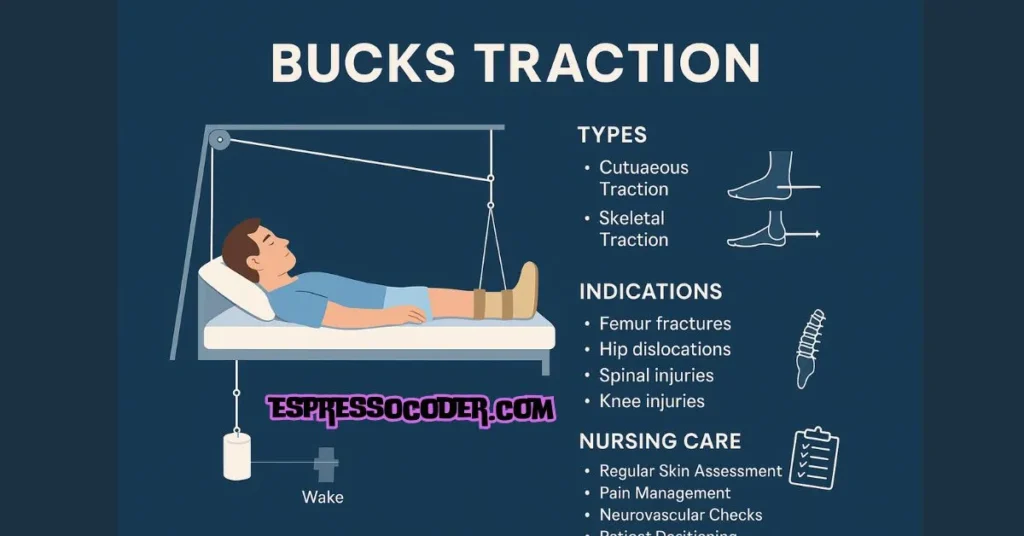
Types of Bucks Traction
Bucks traction is categorized into two primary types:
1. Cutaneous Traction
- Uses adhesive or non-adhesive tapes applied directly onto the skin.
- Suitable for less severe injuries and short-term immobilization.
- Commonly used for elderly patients or when surgical intervention is not immediately feasible.
2. Skeletal Traction
- Involves inserting metal pins or wires directly into the bone.
- Applied in cases requiring greater stability and prolonged immobilization.
- Offers more significant traction force compared to cutaneous methods.
The choice between these types depends on injury severity, patient’s condition, and expected treatment duration.
Setting Up Bucks Traction
Proper setup is essential to ensure effective traction:
- Patient Positioning: The patient is typically placed supine (lying flat on their back).
- Application of Traction Devices: For cutaneous traction, adhesive tapes or foam boots are applied to the limb. In skeletal traction, sterile pins or wires are inserted into the bone under local or general anesthesia.
- Weight Application: Appropriate weights are attached, usually ranging from 5-15 pounds depending on the injury and patient’s size.
- Pulley System: A pulley system maintains constant, controlled tension.
Nursing Care for Patients Undergoing Bucks Traction
Patients undergoing Bucks traction require attentive nursing care, including:
- Regular Skin Assessment: To prevent pressure sores and skin irritation.
- Pain Management: Monitoring and administration of prescribed analgesics.
- Neurovascular Checks: Frequent evaluation of circulation, sensation, and movement.
- Patient Positioning: Regular repositioning and adjustments to maintain comfort and prevent complications.
- Psychological Support: Addressing anxiety and concerns to enhance patient comfort and cooperation.
Bucks Traction vs. Other Traction Methods
Compared to other traction methods, Bucks traction stands out due to its:
- Ease of Application: Requires minimal invasive procedures, reducing patient discomfort and complications.
- Efficiency: Quick setup and rapid stabilization of injuries.
- Patient Comfort: Generally more tolerable, enhancing patient compliance and recovery outcomes.
Alternative traction methods, like Russell traction or skeletal traction alone, may be indicated for specific cases requiring different degrees of immobilization and force.
Potential Complications and Side Effects
Although Bucks traction is generally safe, potential complications can include:
- Pressure Ulcers: Due to prolonged immobilization and pressure on specific areas.
- Nerve Damage: Resulting from excessive or misapplied traction force.
- Circulatory Issues: Blood flow impairment, possibly leading to vascular complications.
- Infection: Particularly with skeletal traction due to pin insertion.
Careful monitoring, preventive measures, and prompt management can mitigate these risks effectively.
Patient Experience and Comfort
Addressing patient concerns about Bucks traction is critical. Healthcare providers must communicate clearly, providing reassurance about the procedure, managing expectations, and explaining its benefits. Comfortable positioning, proper pain management, and psychological support significantly improve the patient experience.
The Role of Bucks Traction in Orthopedics
Bucks traction continues to be indispensable in orthopedic care, particularly for initial management of severe injuries. Its use can reduce the need for immediate surgical intervention, allowing safer and more effective subsequent procedures. Additionally, it significantly enhances patient recovery outcomes through early immobilization and pain control.
Advancements in Traction Techniques
Recent advancements in technology and materials have improved Bucks traction, including:
- Enhanced Traction Devices: More comfortable and skin-friendly materials reducing complications.
- Improved Pulley Systems: Providing consistent and adjustable traction.
- Innovative Monitoring Techniques: Real-time monitoring of traction force and patient response.
These improvements have increased both efficacy and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion
Bucks traction remains a fundamental and effective orthopedic technique. Its non-invasive nature, combined with ongoing advancements, ensures it continues to be widely used and essential in the treatment of orthopedic injuries and conditions. By understanding its applications, procedures, and patient care considerations, healthcare providers can effectively leverage Bucks traction for optimal patient outcomes.
FAQs
1. Is Buck’s traction painful?
Contrary to popular belief, Buck’s traction is not intended to treat or cure orthopedic conditions.
2. How long does a patient typically stay in Buck’s traction?
Buck’s traction is typically used as a stopgap measure until the cause of the problem is identified and a more permanent solution is found.
3. Can Buck’s traction be used for children?
Yes, Buck’s traction is suitable for both adults and children, with adjustments made for paediatric patients.
4. Are there any restrictions on movement during Buck’s traction?
Patients undergoing Buck’s traction are required to remain immobile to maximize the treatment’s efficacy.
5. What is the success rate of Buck’s traction in treating orthopedic conditions?
Buck’s traction is a reliable method for treating orthopedic injuries and conditions, with a high rate of success.

